Дополнительные материалы по программному обеспечению TICRA
Компания TICRA выпускает ряд программных продуктов, предназначенных для анализа рефлекторных антенн методом физической оптики и объединенных в рамках единой среды TICRA Tools: GRASP, ESTEAM (ранее MoM), CHAMP 3D, POS и QUPES, а также пакет SATSOFT, позволяющий выполнить анализ покрытия лучом антенны, оценить параметры луча или многолучевой антенной системы.
Подборка видео на канале Youtube
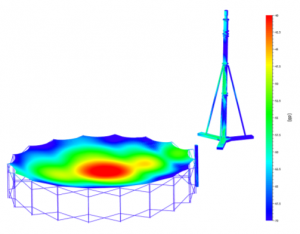
Large European Deployable Reflector: RF Modeling and Measurement Correlation
We present the RF model and correlation with measurements in K band (18.7 GHz) of a 5.1 m diameter deployable reflector antenna in lightweight mesh technology. The RF model includes the manufactured surface shape, electrical properties of the lightweight mesh, a designed and non-circular rim as well as feed tower and truss. Good agreement between main beam shape as well as sidelobe and grating lobe positions between measured and predicted patterns is found.
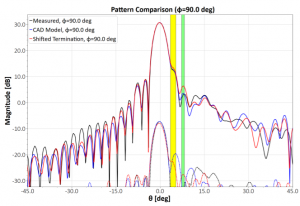
Computational Investigation of the DTU-ESA 12 GHz VAST12 Validation Standard Antenna to Identify Features Contributing to the Radiated Field
In this paper, we present a computational model of the DTU-ESA Standard Validation antenna VAST12, and investigate the impact of how different features on the antenna impact the radiation pattern. It is shown that the termination of the central tube, used to mount the antenna, has a significant impact on the sidelobe level of the antenna.
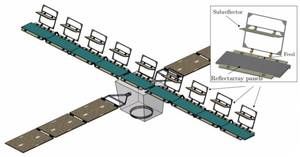
Design of a dual circularly polarized elliptical feed horn for CubeSat reflectarray applications
A low loss dual circularly polarized feed antenna for a high gain deployable K-band reflectarray antenna on a CubeSat platform is designed. The feed consists of an elliptical horn antenna and its feed network, which will be optimized alongside with the reflectarray to match the desired performance goals of the antenna system. The antenna system reaches a peak gain of 38.5 dBi in the 19.7-20.2 GHz band. The gain variation is less than 0.2 dB and the feed reflection coefficient is less than -23.4 dB throughout the bandwidth.
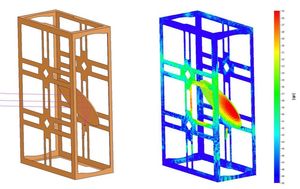
Random surface distortion in GRASP
Surfaces with random distortions are encountered in many practical antenna problems, e.g., when a reflector antenna is manufactured to a specific surface tolerance or it is subjected to wear and tear during its lifetime. As increasingly higher frequencies are used in reflector systems, it becomes more and more important for the antenna engineer to be able to accurately estimate the effects of surface distortions.
In this white paper, we describe how the scattered field from a surface with random distortions can be calculated by GRASP and how these results correspond to the widely used Ruze equations.
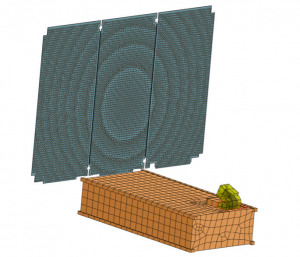
Design of Ka-band Reflectarray antennas for high-resolution SAR instrument
The design of polarization selective reflectarrays for high resolution and wide swath SAR instrument in Ka-band is presented. The antenna system consists of nine dual-offset reflectarray panels, each with the size of 1.5 m×0.55 m. The reflectarrays operate in two modes, a high-resolution mode with a directive beam in one polarization, and a low-resolution mode with a broader beam in the orthogonal polarization. Two designs are presented, a single-layer design and a multilayer design. Both designs provide a gain >46.7 dBi for the high-resolution mode and a gain >45.2 dBi for the low-resolution mode.
Upcoming Along Track Interferometry (ATI) and Ground Moving Target Indication (GMTI) earth observation missions require high resolution and highly sensitive Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) instruments operating on wide swaths and studies have shown, that a single platform Ka-band interferometric SAR instrument is potentially an attractive solution for environmental and security purposes [1], [2]. However, in traditional SAR, high resolution and wide swath are contradictory goals, as a high swath width corresponds to a low pulse repetition frequency (PRF), what leads to a low azimuth resolution. On the other hand, a wide swath width requires a wide antenna beam for proper illumination implying a low antenna gain. In order to achieve an appropriate signal to noise ratio, high transmit powers are necessary, which are beyond current technology limits in Ka-band. In addition, low transmit powers are desirable with respect to power consumption and thermal issues on the spacecraft.
Antennas on CubeSat platforms: Accurate RF predictions
A typical 3U and 6U CubeSat hosting antennas ranging from the low UHF to the higher Ka band are modelled in the ESTEAM software package. The antennas are inspired by recent designs published in the literature.
RF performances of the antennas installed on the CubeSats are computed with the MoM/MLFMM full wave analysis method and compared with the ones in the absence of the CubeSat platform.
The results show that the RF performances of the antennas are substantially changed once these are installed on the CubeSats, indicating that platform scattering and coupling with the neighboring antennas must be included and accounted for already in the antenna design phase.
Исследование радиотехнических характеристик зеркальных антенн космических аппаратов
В настоящее время производство космических аппаратов (КА) является важной и конкурентоспособной отраслью современной экономики, имеющей существенную поддержку со стороны государства и являющейся неотъемлемой частью различных сфер деятельности общества. Так, потребители заинтересованы в качественном и непрерывном доступе к спутниковому телевидению, высокоскоростном доступе к интернету, высокоточной спутниковой навигации. Две трети российских КА спроектированы и произведены на предприятии АО «ИСС», являющемся ведущим российским предприятием по созданию КА. Важной частью КА является его полезная нагрузка, в которую входят антенные системы
О приближенном моделировании крупногабаритной МГЗА
Работа посвящена сопоставлению результатов моделирования многолучевой гибридно-зеркальной антенны с расчетами, полученными в среде Ticra Grasp. Проведена количественная оценка точности моделирования. На геостационарных спутниках систем связи широко применяются крупногабаритные многолучевые гибридные зеркальные антенны (МГЗА) [1−3], к стабильности диаграмм направленности (ДН) которых предъявляются жесткие требования. Публикации [4-6] посвящены стабилизации характеристик антенны, подвергающейся эксплуатационным нагрузкам. В них МГЗА моделировалась в рамках первого приближения [7].