Дополнительные материалы по программному обеспечению Remcom
XFdtd — программное обеспечение компании Remcom Inc. для электромагнитного моделирования с очень широким спектром применений в радиочастотных цепях, антеннах, военном деле/обороне, медицинской ЭМ, фотонике, радиолокации, компонентах, метаматериалах и смежных областях. Представляет собой метод конечных разностей во временной области основанный на дискретизации уравнений Максвелла, записанных в дифференциальной форме
Подборка видео на канале Youtube
Computation of Fields and SAR for MRI with Finite-difference, Time-domain Software
In most fields today, electronic devices must meet strict certification requirements to ensure that humans are not exposed to excessive levels of radiated energy. If sufficiently high levels of power, quantified as the Specific Absorption Rate (SAR), are dissipated in human tissue, the result could be tissue heating and damage. Should a device that has reached the prototyping stage fail to pass SAR certification, a redesign will be required, costing both time and money. Through advanced software tools, designs can be iterated and validated for compliance, ensuring a good product before any prototypes are built. To adequately analyze this type of design, a fully three-dimensional approach for simulating the propagation of electromagnetic fields is required.
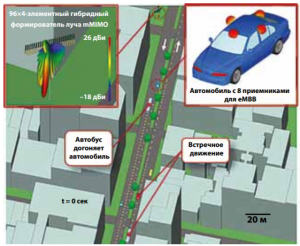
Формирование диаграммы направленности для волн миллиметрового диапазона в реальных сценариях городских условий
СВЧ-электроника 2021'3
При переходе систем связи 5G и 6G в диапазон миллиметровых волн (mmWaves) будут доступны не только новые полосы частот с высокой пропускной способностью, но и поддержка многих новых концепций, предусмотренных для будущих приложений беспроводной связи. Однако потери при распространении и замирания, характерные для таких коротких электромагнитных волн, и намного большее число подключенных мобильных устройств создают проблемы для новых технологий сотовой связи. Решить некоторые из этих проблем может использование антенных системы MIMO и формирование луча диаграммы направленности. Но данное решение должно иметь возможность адаптироваться к динамическим переключениям каналов при перемещении устройств между сотами и взаимодействии сигналов с людьми и движущимися транспортными средствами. Для того чтобы оценить производительность канала с учетом ожидаемого в условиях городской среде распространения волны и влияние доплеровского сдвига частотного спектра, а также оценить воздействие динамического канала на формирование луча MIMO поможет моделирование трассы распространения сигнала.
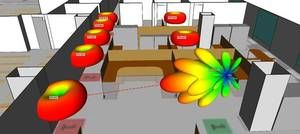
5G mmWave Channel Modeling with Diffuse Scattering in an Office Environment
The millimeter wave frequencies being planned for 5G systems pose challenges for channel modeling. At these frequencies, surface roughness impacts wave propagation, causing scatter in non-specular directions that can have a large effect on received signal strength and polarization. To accurately predict channel characteristics for millimeter wave frequencies, propagation modeling must account for diffuse scattering effects. Wireless InSite’s diffuse scattering capability is based on Degli-Esposti’s work. It includes three models that provide alternative scattering patterns and account for partial cross-polarization of the scattered fields. It also allows the user to optionally sum scattered contributions assuming coherent phase, so that phase effects over closely-spaced antennas (e.g., MIMO) can be accounted for.
This example uses Wireless InSite’s diffuse scattering capability to perform simulations of an indoor wireless network and compares to some measurements detailed in [1]. The scenario, shown in Figure 1, is a portion of the 9th floor of an office building, which includes walls, pillars, windows, cubicle partitions, desks, and cabinets. The transmitter is located at ceiling level in a large, open room. The receivers are located at several points in the room and down the hallway.
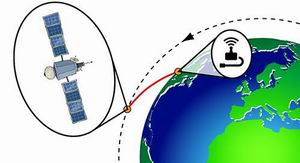
Providing Narrowband IoT Coverage with Low Earth Orbit Satellites
Kenneth M. O’Hara, Gregory J. Skidmore, MWJ 2019'12
This article describes the modeling of a SATCOM link, specifically the use case of using a satellite overlay to extend service continuity to IoT devices in a poorly covered rural area. Non-terrestrial wireless networks (e.g., satellite constellations or high altitude platforms) have unique advantages—wide area service coverage and long-term reliability — which make them important components in the heterogeneous 5G global system of networks. Non-terrestrial networks (NTN) will likely play a critical role providing service to locations not covered by terrestrial 5G networks, such as rural and remote areas, moving platforms and disaster-stricken zones. One use case for NTNs is providing service continuity for machine-to-machine (M2M) or IoT devices as they move out of 5G terrestrial network coverage.1 This is particularly important for M2M/IoT devices which provide critical communications (e.g., applications in eHealth or vital asset tracking).
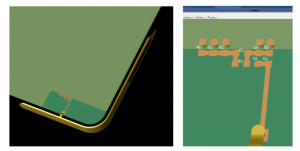
FDTD Simulation: Optimizing an LTE Antenna's Matching Network
A simple antenna for LTE band operation is added to the PC board of a smartphone in XFdtd and the matching circuit is tuned for operation in multiple frequency bands. The components in the matching network are chosen to maximize system efficiency. Figure 1 shows the antenna being used, which is a simple strip fed off center. It can be thought of as two back-to-back inverted L antennas of different “top” lengths, though the operating modes are more complicated than that. Figure 2 shows system efficiency for this antenna when fed directly and demonstrates that matching is required to improve performance.
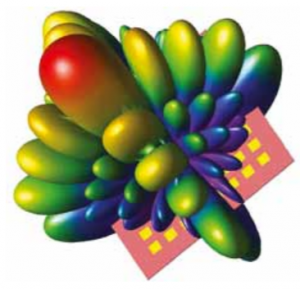
Использование ИФР ЭИИМ для оценки диаграммы направленности антенны миллиметрового диапазон
Сети мобильной связи 5-го поколения призваны решить три основные задачи: увеличить пропускную способность, уменьшить задержку и обеспечить подключение как можно большего числа устройств. Для решения этих задач используются частоты миллиметрового диапазона волн с большой шириной полосы канала [7]. Вопросы применения диапазонов 28 и 38 ГГц рассматриваются в релизе 15 спецификации 3GPP 5G. Недостатком этих диапазонов является сравнительно большое затухание сигнала даже в нормальных условиях, не говоря уже о затухании при атмосферных осадках и в средах с высокой отражательной способностью, особенно при использовании больших ячеек за пределами плотной городской застройки [1].
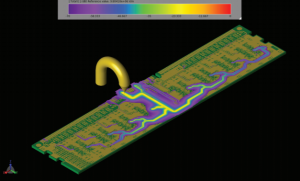
Time Domain Simulation of Electrostatic Discharge Testing
An electrostatic discharge (ESD) is the sudden flow of current between two electrically charged objects, caused by the break-down of the dielectrics separating them, i.e., dielectric breakdown. In the case of electronic devices, the resulting current flow and possible spark can permanently damage the device (see Figure 1). An often recited yet unsubstantiated quote is “…losses associated with ESD in the electronics industry are estimated at between half a billion and $5 billion annually.” In reality, estimating the exact cost of ESD loss is extremely difficult; nonetheless, ESD forces the development and testing of many hardware prototypes during design and manufacturing and contributes to a high number of warranty claims with loss of consumer confidence if a failure occurs in the hands of the consumer. Therefore, electronics manufacturers go to great lengths to properly shield sensitive components and design systems to reduce, dissipate and neutralize static charge.
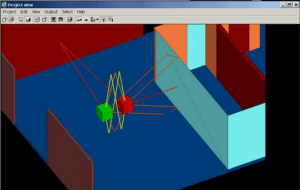
Моделирование и алгоритмизация решения задач в беспроводных системах связи в условиях замкнутых пространств
МОИТ, 2017'3
Актуальность исследования обусловлена тем, что в современных условиях наблюдается повсеместное использование беспроводных сетей. При проектировании беспроводных сетей большая роль отводится этапу моделирования, в который входит проведение расчетов по основным параметрам системы беспроводного доступа. В связи с этим, данная статья направлена на выявление возможностей использования соответствующих подходов при моделировании распространении радиосигналов в помещениях, и на определение возможных ошибок в расчетах. Ведущим подходом к исследованию данной проблемы является использование метода трассировки лучей, позволяющем учитывать различную геометрию помещений и материалов, располагаемых внутри объектов. В статье представлены результаты моделирования в программе Wireless InSite. Материалы статьи представляют практическую ценность для специалистов, связанных с проектированием беспроводных сетей внутри помещений.
Программное обеспечение для планирования радиосетей
Программный пакет Wireless InSite был разработан компанией Remcom (www.remcom.com) специально для оценки распространения электромагнитного излучения на больших пространствах: городских кварталах, сельской местности и на горном или равнинном ландшафте. Особенностью пакета является возможность быстрого моделирования при наличии нескольких передатчиков и приемников сигналов с антеннами различных типов. Быстродействие программы позволяет получить качественные результаты анализа при изменении положения антенн, а также формы и высоты окружающих объектов.